leakview
Overview
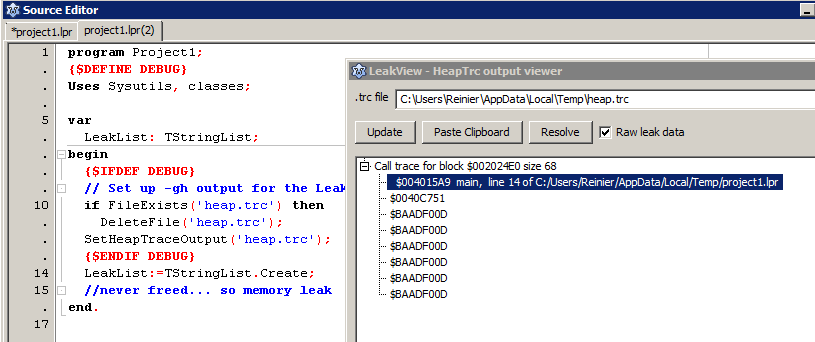
Leakview (Tools/Leak View or Tools/Find source lines for leak/stack-traces in Lazarus 1.3+) allows fast navigation trough HeapTrc leak reports.
Usage
Leakview reads heaptrc output. For this to work, you'll need to enable heaptrc in your code:
Enabling heaptrc in Lazarus
To enable this in your Lazarus project: go to Project Options/Linking and in the Debugging section enable Use Heaptrc unit (check for mem-leaks) (-gh)
You can then let the program log the output of the heaptrc unit to a file. Add the following code fragments in your .lpr, at the beginning of your code to redirect the heaptrc output to file:
{$DEFINE debug} // do this here or you can define a -dDEBUG in Project Options/Other/Custom Options, i.e. in a build mode so you can set up a Debug with leakview and a Default build mode without it
uses
...
{$IFDEF debug}
, SysUtils
{$ENDIF}
...
begin
{$IFDEF DEBUG}
// Assuming your build mode sets -dDEBUG in Project Options/Other when defining -gh
// This avoids interference when running a production/default build without -gh
// Set up -gh output for the Leakview package:
if FileExists('heap.trc') then
DeleteFile('heap.trc');
SetHeapTraceOutput('heap.trc');
{$ENDIF DEBUG}
...
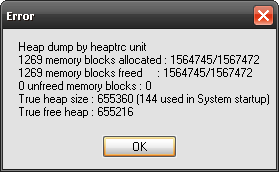
end.On Unix systems the leakview results are stored in a file the path of which is specified. Windows displays dialog boxes like the following example:
Enabling heaptrc in FPC
In FPC, you can specify -gh in your compiler options or include the heaptrc unit in your uses clause (as one of the first items).
Then redirect the heaptrc output to file (instead of standard output). You can use similar code to the Lazarus code or alternatively, set the environment variable, e.g. on *nix:
export HEAPTRC="log=heap.trc"
or Windows:
set HEAPTRC="log=heap.trc"