Difference between revisions of "Dialog Examples/ru"
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
===MessageDLG=== | ===MessageDLG=== | ||
| − | <syntaxhighlight>function MessageDlg(const aMsg: string; DlgType: TMsgDlgType; | + | <syntaxhighlight>function MessageDlg(const aMsg: string; DlgType: TMsgDlgType; Buttons: TMsgDlgButtons; HelpCtx: Longint): Integer; |
| − | + | function MessageDlg(const aCaption, aMsg: string; DlgType: TMsgDlgType; Buttons: TMsgDlgButtons; HelpCtx: Longint): Integer;</syntaxhighlight> | |
| − | function MessageDlg(const aCaption, aMsg: string; DlgType: TMsgDlgType; | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Две версии этой функции, то есть первый параметр 'Caption' является необязательным; если пропущено, заголовок отсутствует в поле | |
| − | + | Это наиболее полный и продуманный диалог сообщений, который позволяет программисту значительно контролировать внешний вид диалогового окна. | |
| − | + | Параметры, определяющие тип поля и его значка, являются типами, а не целочисленными константами, и кнопки можно указывать в виде набора в квадратных скобках, например [mbRetry, mbIgnore, mbAbort, mbCancel]. | |
| − | + | Параметр HelpCtx в настоящее время не реализован и должен быть установлен в ноль. | |
| − | + | Возвращаемое значение из функции - это идентификатор нажатой кнопки, выраженный в виде целого числа (см. определения ниже, [mrNone..mrAll]). | |
| − | + | Пример: | |
<syntaxhighlight>uses | <syntaxhighlight>uses | ||
| Line 111: | Line 109: | ||
end;</syntaxhighlight> | end;</syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | [[image:Question.png|bottom]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== QuestionDlg === | === QuestionDlg === | ||
Revision as of 13:42, 12 April 2019
│
Deutsch (de) │
English (en) │
español (es) │
suomi (fi) │
français (fr) │
日本語 (ja) │
polski (pl) │
русский (ru) │
slovenčina (sk) │
中文(中国大陆) (zh_CN) │
Несколько полезных диалогов
Вот некоторые полезные диалоги, которых нет в палитре компонентов:
- procedure ShowMessage (const Msg: string);
- function MessageBox (Text, Caption : PChar; Flags: Word): Integer;
- function MessageDlg (const Msg: string; AType: TMsgDlgType; AButtons: TMsgDlgButtons; HelpCtx: LongInt): Word;
- function InputBox (const ACaption, APrompt, ADefault: string); string;
- function InputQuery (const ACaption, APrompt: string; var Value: string): Boolean;
- function PasswordBox(const ACaption, APrompt : String) : String;
Каждый из этих компонентов приводит к отображению небольшого всплывающего окна, которое содержит некоторую информацию и требует ответа пользователя: либо нажатия кнопки, либо ввода текста, либо и то и другое. Программист практически не контролирует формат, размер или положение этих всплывающих окон, но может влиять на их текстовое содержимое.
Причина, по которой часто существует несколько очень похожих альтернатив, заключается в том, что разные методы могут вызывать компонент и получать данные обратно из процедуры или функции. Эти диалоги могут быть «платформозависимыми», то есть они могут отображаться по-разному. Например, строки, которые полностью отображаются в Windows XP, могут быть усечены в Windows 7.
Диалоги сообщений
Диалоги сообщений отображают сообщение и ждут реакции [пользователя в виде] нажатия клавиши или щелчка мыши.
ShowMessage
{ Определено в Dialogs.pp }
procedure ShowMessage(const Msg: string);Простейшее диалоговое окно сообщения: принимает в качестве параметра простую строку, отображает ее в стереотипном поле и ожидает события щелчка мышью или клавиши ввода, прежде чем вернуться к вызывающей подпрограмме или программе.
Это модальный вызов процедуры, то есть окно отображается, получает фокус и не оставляет фокус, пока не будет нажата кнопка ОК или не выбрано что-либо иное.
Пример:
program LazMessage;
uses
Dialogs;
begin
ShowMessage('Это сообщение от Lazarus');
end.У вас есть возможность создавать многострочные сообщения, используя следующие разделители строк, все они будут работать:
- sLineBreak
- LineEnding
- или код символьный код: #13#10
Пример из нескольких строк:
program LazMessage;
uses
Dialogs;
begin
ShowMessage('Это - многострочное' + sLineBreak + 'сообщение!' );
end.MessageBox
{ Определено в Forms.pp как часть TApplication; следовательно, должно вызываться как Application.Messagebox()
или с использованием конструкции 'with Application do ...'}
function Application.MessageBox(Text, Caption: PChar; Flags: LongInt): Integer;Параметры включают
- Text: строка, которая отображается как приглашение или инструкция в поле;
- Caption: строка заголовка в верхней части окна сообщения;
- Flags: longint - целое число, построенное путем сложения различных констант, для определения содержимого и поведения блока, например, MB_ABORTRETRYIGNORE + MR_ICONQUESTION заставит приложение отображать значок запроса (?) в поле с тремя кнопками: ABORT RETRY IGNORE.
Функция возвращает целочисленное значение, соответствующее нажатой кнопке; его значение может быть определено с помощью констант[IDOK..IDHELP] Она может быть вызвана как вызов процедуры (то есть как оператор 'MessageBox()', а не как вызов функции 'Variable:= MessageBox()' - см. Пример ниже)
Пример:
uses
Forms, Dialogs, LCLType;
procedure DisplayMessageBox;
var
Reply, BoxStyle: Integer;
begin
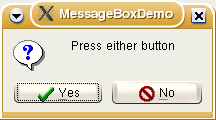
BoxStyle := MB_ICONQUESTION + MB_YESNO;
Reply := Application.MessageBox('Press either button', 'MessageBoxDemo', BoxStyle);
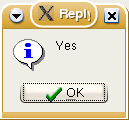
if Reply = IDYES then Application.MessageBox('Yes ', 'Reply',MB_ICONINFORMATION)
else Application.MessageBox('No ', 'Reply', MB_ICONHAND);
end;Обратите внимание, что в этом примере строки 'Yes' и 'No' были дополнены пробелами; в противном случае поле не будет достаточно широким, чтобы правильно отображать заголовок
MessageDLG
function MessageDlg(const aMsg: string; DlgType: TMsgDlgType; Buttons: TMsgDlgButtons; HelpCtx: Longint): Integer;
function MessageDlg(const aCaption, aMsg: string; DlgType: TMsgDlgType; Buttons: TMsgDlgButtons; HelpCtx: Longint): Integer;Две версии этой функции, то есть первый параметр 'Caption' является необязательным; если пропущено, заголовок отсутствует в поле
Это наиболее полный и продуманный диалог сообщений, который позволяет программисту значительно контролировать внешний вид диалогового окна. Параметры, определяющие тип поля и его значка, являются типами, а не целочисленными константами, и кнопки можно указывать в виде набора в квадратных скобках, например [mbRetry, mbIgnore, mbAbort, mbCancel]. Параметр HelpCtx в настоящее время не реализован и должен быть установлен в ноль. Возвращаемое значение из функции - это идентификатор нажатой кнопки, выраженный в виде целого числа (см. определения ниже, [mrNone..mrAll]).
Пример:
uses
Forms, Dialogs, LCLType, Controls;
procedure TryMessageDlg;
begin
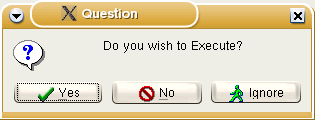
if MessageDlg('Question', 'Do you wish to Execute?', mtConfirmation,
[mbYes, mbNo, mbIgnore],0) = mrYes
then { Execute rest of Program };
end;QuestionDlg
Question dialog allows changing button captions and setting default and cancel buttons. Example:
case QuestionDlg ('Caption','Message',mtCustom,[mrYes,'Positive', mrNo, 'Negative', 'IsDefault'],'') of
mrYes: QuestionDlg ('Caption','So you mean „Yes“',mtCustom,[mrOK,'That is right'],'');
mrNo: QuestionDlg ('Caption','Oh, you mean „No“',mtCustom,[mrOK,'Exactly'],'');
mrCancel: QuestionDlg ('Caption','You canceled the dialog with ESC or close button.',mtCustom,[mrOK,'Exactly'],'');
end;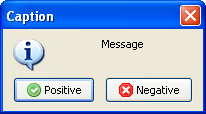
Advanced examples for buttons (from promptdialog.inc)
[mrOk,mrCancel,'Cancel now',mrIgnore,300,'Do it','IsDefault']This will result in 4 buttons:
- 'Ok' returning mrOk
- 'Cancel now' returning mrCancel
- 'Ignore' returning mrIgnore
- 'Do it' returning 300. This will be the default button (focused)
Usually buttons in Lazarus dialogs have icons. In order to prevent icons from being shown non standardize values for message results can be used. Currently highest standardized value is 11. For example:
case QuestionDlg ('Caption','Message',mtCustom,[20,'Positive', 21, 'Negative',22,'I do not know','IsCancel'],'') of
20: QuestionDlg ('Caption','So you mean „Yes“',mtCustom,[20,'That is right'],'');
21: QuestionDlg ('Caption','Oh, you mean „No“',mtCustom,[21,'Exactly'],'');
22: QuestionDlg ('Caption','So, please find out!',mtCustom,[22,'Maybe'],'');
end;In order to facilitate work, constants can be defined. For example:
const
mrNoneNI= 20;
mrOkNI= mrNoneNI+1;
mrCancelNI= mrNoneNI+2;
mrAbortNI= mrNoneNI+3;
mrRetryNI= mrNoneNI+4;
mrIgnoreNI= mrNoneNI+5;
mrYesNI= mrNoneNI+6;
mrNoNI= mrNoneNI+7;
mrAllNI= mrNoneNI+8;
mrYesToAllNI= mrNoneNI+10;
mrCloseNI= mrNoneNI+11;
mrLastNI= mrCloseNI;
begin
case QuestionDlg ('Caption','Message',mtCustom,[mrYesNI,'Positive', mrNoNI, 'Negative',mrCancelNI,'I do not know','IsCancel'],'') of
mrYesNI: QuestionDlg ('Caption','So you mean „Yes“',mtCustom,[mrYesNI,'That is right'],'');
mrNoNI: QuestionDlg ('Caption','Oh, you mean „No“',mtCustom,[mrNoNI,'Exactly'],'');
mrCancelNI: QuestionDlg ('Caption','So, please find out!',mtCustom,[mrCancelNI,'Maybe'],'');
end; //case
end;Text input Dialogs
InputBox
Text input Dialogs: display a message and await user text input
function InputBox(const ACaption, APrompt, ADefault: String): String;Displays a box with defined title and prompt, and expects user input in a text box. A default string can optionally be displayed in the text box. The user-entered or default string is returned as the function result.
Example:
uses
Forms, LCLType, Dialogs, Controls;
procedure TryInputBox;
var
UserString: string;
begin
UserString := InputBox('Get some text input',
'Please type in some information', 'Some sample text');
ShowMessage(UserString)
end;InputQuery
function InputQuery(const ACaption, APrompt : String;
MaskInput : Boolean; var Value : String) : Boolean;
function InputQuery(const ACaption, APrompt : String;
var Value : String) : Boolean;Two versions of this function which displays a prompt and expects user input of textual data; the first includes a MaskInput boolean parameter which determines whether the user input is masked out by asterisks in the text-input box (like during entry of a password), while the second omits this property. The text entered by the user is returned in the variable parameter 'Value'; the function result is a boolean which returns TRUE if the OK button was pressed, or FALSE if the box was closed by any other mechanism (such as clicking the 'Close' icon on the top title bar). Omitting the MaskInput parameter is equivalent to setting it FALSE.
Example:
uses
Forms, LCLType, Dialogs, Controls;
procedure TryInputQuery;
var
QueryResult: Boolean;
UserString: string;
begin
if InputQuery('Question', 'Type in some data', TRUE, UserString)
then ShowMessage(UserString)
else
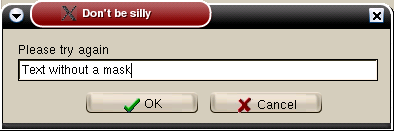
begin
InputQuery('Don''t be silly', 'Please try again', UserString);
ShowMessage(UserString);
end
end;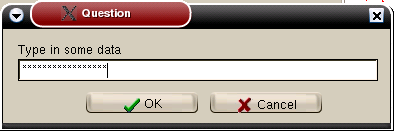
PasswordBox
Function PasswordBox(const ACaption, APrompt : String) : String;Behaves very similarly to the InputQuery function with MaskInput = TRUE; the difference is that the password that was typed in is returned as the result of the function (like InputBox).
Constants and Types used in message dialogs
Several constants and types relevant for use with the dialog boxes are pre-defined in the LCL library:
const { Defined in LCLType.pp }
integer constants for defining the types of buttons and the icon for display in MessageBox
MB_OK = $00000000;
MB_OKCANCEL = $00000001;
MB_ABORTRETRYIGNORE = $00000002;
MB_YESNOCANCEL = $00000003;
MB_YESNO = $00000004;
MB_RETRYCANCEL = $00000005;
MB_ICONHAND = $00000010;
MB_ICONQUESTION = $00000020;
MB_ICONEXCLAMATION = $00000030;
MB_ICONASTERICK = $00000040;
MB_ICONWARNING = MB_ICONEXCLAMATION;
MB_ICONERROR = MB_ICONHAND;
MB_ICONINFORMATION = MB_ICONASTERICK;integer constants defining the return value from MessageBox according to which button was pressed
IDOK = 1; ID_OK = IDOK;
IDCANCEL = 2; ID_CANCEL = IDCANCEL;
IDABORT = 3; ID_ABORT = IDABORT;
IDRETRY = 4; ID_RETRY = IDRETRY;
IDIGNORE = 5; ID_IGNORE = IDIGNORE;
IDYES = 6; ID_YES = IDYES;
IDNO = 7; ID_NO = IDNO;
IDCLOSE = 8; ID_CLOSE = IDCLOSE;
IDHELP = 9; ID_HELP = IDHELP;define whether first, second or third button is default
MB_DEFBUTTON1 = $00000000;
MB_DEFBUTTON2 = $00000100;
MB_DEFBUTTON3 = $00000200;
MB_DEFBUTTON4 = $00000300;The Flags parameter of MessageBox is constructed by adding a button constant [MB_OK..MB_RETRYCANCEL], an optional icon constant [MB_ICONHAND..MB_ICONINFORMATION] and an optional default button constant [MB_DEFBUTTON1..MB_DEFBUTTON3]
Types for use in MessageDlg, which needs parameters AType of TMsgDlgType and AButtons of TMSgDlgButtons
{ Defined in Dialogs.pp }
type
TMsgDlgType = (mtWarning, mtError, mtInformation, mtConfirmation,
mtCustom);
TMsgDlgBtn = (mbYes, mbNo, mbOK, mbCancel, mbAbort, mbRetry, mbIgnore,
mbAll, mbNoToAll, mbYesToAll, mbHelp, mbClose);
TMsgDlgButtons = set of TMsgDlgBtn;
const
mbYesNoCancel = [mbYes, mbNo, mbCancel];
mbOKCancel = [mbOK, mbCancel];
mbAbortRetryIgnore = [mbAbort, mbRetry, mbIgnore];
MsgDlgBtnToBitBtnKind: array[TMsgDlgBtn] of TBitBtnKind = (
bkYes, bkNo, bkOK, bkCancel, bkAbort, bkRetry, bkIgnore,
bkAll, bkNoToAll, bkYesToAll, bkHelp, bkClose
);
BitBtnKindToMsgDlgBtn: array[TBitBtnKind] of TMsgDlgBtn = (
mbOk, mbOK, mbCancel, mbHelp, mbYes, mbNo,
mbClose, mbAbort, mbRetry, mbIgnore, mbAll, mbNoToALl, mbYesToAll
);
{ Defined in Controls.pp }
const
mrNone = 0;
mrOK = mrNone + 1;
mrCancel = mrNone + 2;
mrAbort = mrNone + 3;
mrRetry = mrNone + 4;
mrIgnore = mrNone + 5;
mrYes = mrNone + 6;
mrNo = mrNone + 7;
mrAll = mrNone + 8;
mrNoToAll = mrNone + 9;
mrYesToAll = mrNone + 10;
mrLast = mrYesToAll;